History of Standards New Zealand
From humble beginnings based on tragedy to setting standards protecting the lives and livelihoods of today’s New Zealanders.
2024: Pacific Islands Standards Week
- Standards New Zealand hosted the second ever Pacific Islands Standards Week event. This brought together around 40 representatives from across the Pacific Islands to enable learning and professional development in the standards and conformance system. This is part of a wider three year project funded by MFAT.
2021-2025: sponsored guidance for energy efficiency
- EECA (the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority) sponsored the development and free access of a range of change enabling publicly available specifications (PAS) supporting EV charging, integration of smart home technologies, efficient heat pumps and biomass boilers. If used by consumers and installers these could help people save energy and money.

Born from the devastation of the 1931 Napier quake, Standards New Zealand’s history charts decades of international engagement, progress, partnership and growth. Since the first New Zealand standard for Number 8 wire, standards have become the backbone of regulatory change and trusted good practice.
2022: 90 years of improving standards for a better New Zealand
- Standards New Zealand marks the 90th year since New Zealand’s first dedicated council gathered to set the path for raising standards.
2021: A year in numbers
- In March, a new logo and website improved accessibility, modernised Standards New Zealand’s brand, and simplified information for the 680,000 annual website visitors.
- More than 80,000 standards sold.
- Our website provides access to 143,000+ standards. These include historical, superseded and withdrawn standards, as well as 2762 current New Zealand standards and tens of thousands of international and joint Australian/New Zealand standards and international adoptions.
- 321 international standards committees.
- More than 115 New Zealand or joint (AS/NZ) standards cited in legislation.
- 168,000 downloads of the 131 sponsored standards.
2021: Ngā paerewa guides culturally appropriate healthcare
- Published, with sponsorship by Health NZ for free download, NZS 8134:2021 Ngā Paerewa Health and disability services standard which consolidates three previous separate standards and incorporates key health-related Māori cultural considerations for culturally appropriate care.
2018: Innovation explored
- To keep standards responsive to users’ needs, Standards New Zealand began working with external partners to find ways for users to apply standards practices through digital tools. This formed our digital products licensing service.
2017: First sponsored standards
- Standards New Zealand set the path for easy access to standards with the sponsorship of free-to-access standards to support compliance. Building System Performance (BSP, the building regulator) sponsored 126 standards to support compliance with the New Zealand Building Code. Other sponsors included the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority (EECA, the energy regulator) to support the adoption of energy efficient technologies, and the Ministry of Health to support consistent health care and better Māori cultural inclusion.
2016: Move into MBIE
- Under the Act Standards New Zealand became a business unit within the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE) in March 2016.
2015: Governance structure, process and funding model formalised in new Act
- The Standards and Accreditation Act 2015 formalised the structure and delegation authority of the New Zealand Standards Executive and Standards Approval Board, and cost-recovery model.
2010: Enter social media
- Standards New Zealand joined social media with a LinkedIn page.
1998: Standards Mark sold off
- The certification division was sold to an international business in order to focus on the core purpose of standards development.
1995: SANZ becomes Standards New Zealand
- A fourth renaming saw the emergence of today’s Standards New Zealand as the national standardisation body.
1995: TBT supports international trade
- The Technical Barriers to Trade Agreement (TBT) was established by the World Trade Organisation (WTO) which aimed to ensure that regulations, standards, testing and certification procedures do not create unnecessary obstacles, while also recognising countries’ rights to adopt the standards they consider appropriate. The agreement also sets out a code of good practice for both governments and non-governmental or industry bodies to prepare, adopt and apply voluntary standards.
1988: Standards Act 1988
- This act repealed the Standards Act 1965.

New Standards Council appointed by the Minister of Trade and Industry, Hon. David Caygill, in terms of the Standards Act 1988, held its first meeting on 22 July 1988
In the first 50 years:
- 2,185 New Zealand standards were published
- 2,600 Standard Mark licenses were issued
- Over 1,000,000 hard copy standards were sold
- 130 standing committees, with 1,300 committee members, were formed.

Standards Association of New Zealand advertisement in 1982
1982: Golden Jubilee year
- This marked 50 years of national standards development in New Zealand.

Standards Council in 1982
1981: Government Purchasing Sectional Committee disbanded
- Government departments were instructed to give preference to items made to New Zealand Standards when purchasing goods.
1980: Further international connections made
- The standards associations of Australia and New Zealand met in Christchurch in February to increase trans-Tasman co-operation and plan for joint Australian/New Zealand Standards.
- In November, Exporting to China, a guide to technical requirements and authorities in China, was published following relationship building meetings in China. This was a forerunner to Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT).
1979: IEC membership and modernisation
- The New Zealand Electrotechnical Committee (NZEC) attended IEC’s (International Electrotechnical Commission) IEC’s 44th General Meeting in Sydney, where New Zealand was admitted to full membership of the IEC, 75 years after the IEC was founded.
1978: Help for export and electrotechnical industries
- In June, the Prime Minister, the Rt Hon R D Muldoon, launched the SANZ Technical Help to Exporters (T-H-E) service.
- The first meeting of the New Zealand Electrotechnical Committee (NZEC) took place on 1 September.
- NZS 3604:1978 was published setting the ongoing standard for timber-framed buildings.
1975: Alignment of trans-Tasman manufacturing standards
- At a standards conference in Christchurch, SANZ and the Standards Association of Australia made recommendations on how to improve and expedite the alignment of manufacturing – particularly whitegoods and electrical cabling-standards between Australia and New Zealand.
1973: Pacific partners through PASC
- The Pacific Area Standards Congress (PASC) was established to enable countries on the Pacific rim to have regular consultations on matters of mutual interest.
- The New Zealand Standard Mark was revised.
Revision to the New Zealand Standards Mark
1971: First standard using metric measurements
- Adhering to the ‘new’ metric system NZS 6501 P:1971 The International System (SI) units and their application was published.
- The Standard Certification Mark was revised.
1970: First World Standards Day
- Each year on 14 October, the members of the IEC, ISO, and ITU celebrate World Standards Day, which is a means of paying tribute to the collaborative efforts of the thousands of experts worldwide who develop the voluntary technical agreements that are published as international standards.
1969: Move to metrics
- The Government decided that New Zealand should move to the metric system of weights and measures within 5 to 10 years and the SANZ Metric Advisory Board was set up to encourage, assist and advise on progressive voluntary adoption of the metric system in New Zealand.
1967: International adoptions made easier
- A simplified process for endorsing overseas standards as suitable for use in New Zealand was introduced.
1966: NZSI to SANZ
- The New Zealand Standards Institute ceased to exist on 31 March becoming the Standards Association of New Zealand (SANZ). which reported to a larger and more broadly representative Standards council.

Standards Association of New Zealand SANZ logo
1965: Independence and participation with private sector
- The New Zealand Standards Institute’s work was reviewed. A need for greater involvement of the private sector led to a proposal ‘that the New Zealand Standards Institute should become an independent organisation comprising representatives of consumers, industry, local bodies and the Government, all contributing to its costs in proportions to be determined’.
- The Standards Act 1965 was passed on 22 October.
1963: Standards build on their construction foundations
- Revised parts of the Model Building Bylaw rearranged and reissued as NZSS 1900 Model building bylaw – Basic design loads (precursor to NZS 3604 Timber-framed buildings).
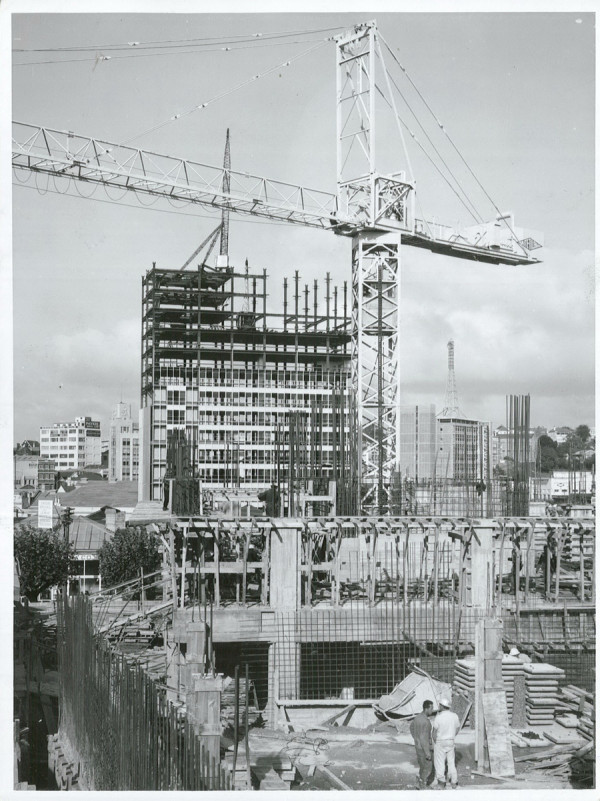

Police administration building under construction in Auckland 1965. Archives New Zealand CC BY 2.0
1961: Electrical Wiring Regulations 1961 passed
- The regulations specified that all electrical apparatus and material used in an electrical installation must comply with the appropriate New Zealand Standard Specification.
- New Zealand Standards Institute committees were established in centres other than Wellington, in a time when there was no other option than physical attendance to participate.
- In June, New Zealand was elected as a member of the ISO council.
In the first 25 years:
- 1,327 New Zealand Standards were issued, with around 80% used in the building and construction sector.
- 381 Standard Mark licences were issued.
1958: Silver jubilee
- The New Zealand Standards Institute marked 25 years since the first New Zealand standard was published and New Zealand-centric standardisation.
1955: Quarterly update
- The first issue of the quarterly New Zealand Standards Bulletin was published. Before times of digital communication this was the main form of communications for users and commissioners of standards for decades.
1950: Standards Amendment Act 1950 passed
- The definition of ‘specification’ was extended to include model bylaws; permit the making of bylaws by adopting standard specifications; and extending offences and penalties to include unauthorised comparison with standards for purposes of gain or profit.
1947: New Zealand joins ISO
- New Zealand was one of the 27 inaugural members of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Today, ISO is a network of 167 national standards bodies bridging public and private sectors, with New Zealand being a participating member on 70 technical committees and an observer on 140.
1944: International partnership grows
- To Farmers Trading Company Limited for school paper stationery.
- New Zealand became a member of the United Nations Standards Co-ordinating Committee (forerunner of the International Organization for Standardization [ISO]).
1942: Standards Mark registered

New Zealand Standards Mark
1941: War and Standards Act
- A War Emergency Council was formed to take over the work of the regular standards council in preparing war emergency standards and remained in place until 1945. The first war emergency standard is published – NZSS E1 Stretchers for ambulance purposes.
- The Standards Act 1941 is passed – a world first giving statutory authorisation and status to standard specifications.

First New Zealand Standards Act 1941 front page of Act document
1938: First original New Zealand Standard published
- Reflecting Kiwi ingenuity, our first original standard was NZSS 143 – Galvanised (zinc coated) steel fencing wire, for ‘number 8 wire’.
1936: NZSI to NZSI
- The New Zealand Standards Institution was dissolved and the New Zealand Standards Institute (NZSI) established as an independent body within the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research.
1934: Standards take root in the building code
- Government asked the New Zealand Standards Institution to draft a Model Building Bylaw based on the basic code prepared by the Building Regulations Committee.
1933: First New Zealand standard issued
- The first New Zealand standard, NZSS 1 (BSS 467:1932) The colouring and marking of foundry patterns, was issued. It was based on a British standard– and 90 years later, thousands of standards used across New Zealand industries are still based on international practices.
1932: Birth of New Zealand Standards Institute
- As a result of a visit by the director of the British Standards Institution (BSI), Mr Charles le Malstre, a standards organisation was set up In New Zealand with the support of the New Zealand Society of Civil Engineers. This organisation was known as the New Zealand Standards Institution and on 7 July the newly formed Council met for the first time.
Napier earthquake 3 February 1931
- The devastating loss of life from inadequate building design and construction methods prompted the government to set up a Building Regulations Committee, which recommended that a national uniform building code be prepared and applied to bring standards to new construction.
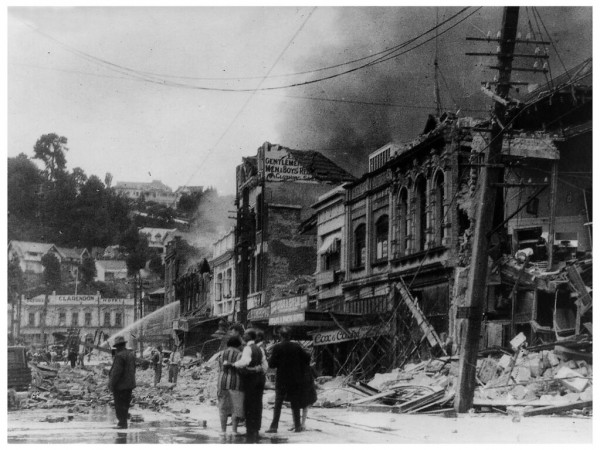

1931 Hawkes Bay earthquake and subsequent damage to Clarendon Hotel on Shakespeare Road. Archives NZ CC BY 2.0
Pre-1931: Precursor to standards in New Zealand
- ln 1920 a committee to review and comment on draft British Standards was set up In New Zealand by the British Engineering Standards Association (forerunner of the British Standards Institution). British standards would be the go-to for more than a decade.
